Last Updated on 3 months ago by Gila

The Step-by-Step Guide to Effective Email Deliverability and Inbox Placement
Introduction:
You’ve mastered segmentation, built high-converting landing pages, and set up your welcome automation. But all that work is wasted if your emails land in the spam folder.
Email Deliverability Guide is the ability of your email to successfully reach the recipient’s main inbox (not their spam folder or promotions tab). Your deliverability is controlled by your Sender Reputation, which is a score given to you by providers like Gmail, Yahoo, and Outlook.
This guide provides the simple, non-negotiable, 5-step checklist to protect your Sender Reputation and ensure your emails reach the inbox every time.
TL;DR: Email deliverability is about proving you are a real sender, mailing only engaged subscribers, and sending steady, relevant emails so inbox providers trust you.
- Authenticate your domain with SPF, DKIM, and DMARC so Gmail and Outlook know you’re legitimate.
- Keep your list clean: remove hard bounces, honor unsubscribes, and use a clear sunset policy.
- Avoid spammy words, all caps, and image-only emails; focus on simple, reader-friendly content.
- Send at a consistent pace and warm up new domains slowly instead of blasting huge volumes.
- Monitor hard bounces, spam complaints, unsubscribes, and click-through rates regularly.
- Use tools like Google Postmaster Tools and mail-tester.com to spot problems before they grow.
Part 1: Step 1: Technical Foundation (Prove You Are Real)
The first step is proving to mailbox providers (ISPs) that you are a legitimate sender and not a scammer trying to “spoof” (fake) your domain name. This is done through Email Authentication.
The 3 Non-Negotiable DNS Records
You must set up these three records within your domain’s DNS settings (your email provider will give you the exact text):
| Record | What It Does | Analogy for Novices |
| SPF (Sender Policy Framework) | Tells the world which servers are allowed to send mail on your behalf. | The Guest List. It says, “Only these servers are allowed to be at the party.” |
| DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) | Adds an encrypted, hidden signature to your email that verifies the content hasn’t been tampered with during transit. | The Wax Seal. It proves the message came from you and wasn’t changed. |
| DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication) | Tells the receiving server what to do if the SPF or DKIM fails (e.g., “send it to spam”). | The Security Guard. It enforces the rules set by SPF and DKIM. |
Action Item: Ask your email service provider (ESP) or domain host for their specific SPF and DKIM records and insert them into your DNS.

Once your technical foundation is in place, these guides can help you choose and use the right tools with confidence:
Part 2: Step 2: Maintain List Hygiene (Quality Over Quantity)
A healthy list is the biggest factor in long-term deliverability. Sending to unengaged or non-existent email addresses tells Gmail that your emails are unwanted, which destroys your reputation.
To keep your list healthy and engaged, it helps to combine good hygiene with steady, thoughtful growth:
1. Remove Hard Bounces Immediately
A Hard Bounce means the email address does not exist (it is invalid or fake).
- The Rule: Any email address that produces a hard bounce must be immediately and permanently removed from your list. Most quality ESPs (like MailerLite, Klaviyo) do this automatically.
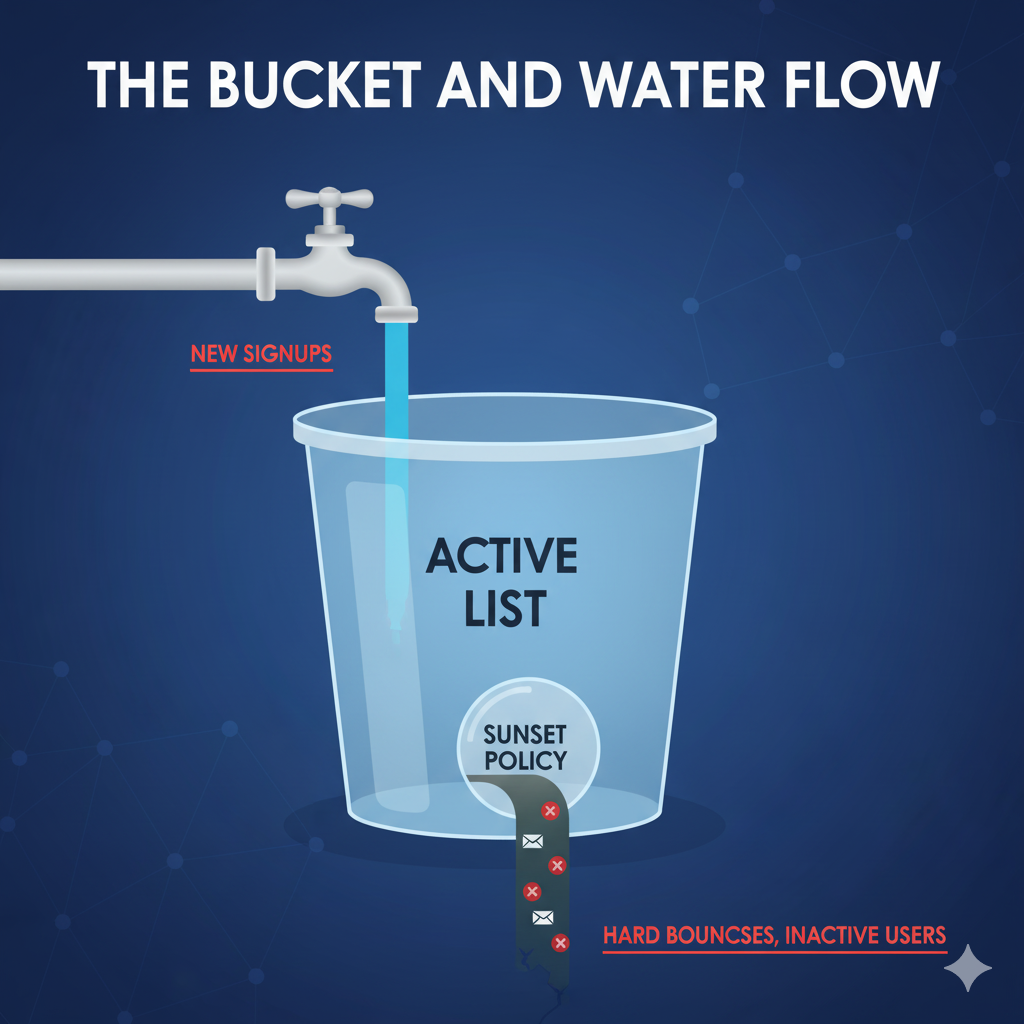
2. Implement a Sunset Policy
A Sunset Policy is your rule for deleting inactive subscribers.
- The Action: Define “inactive” (e.g., has not opened or clicked an email in 6 to 12 months). Run a re-engagement campaign to them (a last-ditch “We Miss You” email). If they still don’t engage, remove them from your active mailing list.
- The Why: A list of 1,000 engaged subscribers is far more valuable than a list of 10,000 subscribers, 9,000 of whom never open your emails.
3. Never Buy a List
Bought lists are often filled with spam traps (fake email addresses used by ISPs to catch spammers). Hitting just one spam trap can immediately blacklist your domain.
Part 3: Step 3: Optimize Content and Engagement
Your content is the engagement signal that ISPs prioritize. High engagement = Good Reputation.
Better engagement starts with clear, helpful content that fits into your bigger online business plan:
1. Avoid Spam Trigger Words
Certain words and formats will flag your email for spam filters.
- Bad Words to Avoid: “Free,” “Cash,” “Winner,” “Urgent,” “Opportunity,” excessive use of dollar signs ($$) or exclamation marks (!!!).
- Bad Formatting: Do not use ALL CAPS in your subject line. Avoid sending emails that are just one large image with minimal text (aim for a 60% text to 40% image ratio).
2. Make it Easy to Unsubscribe
This sounds counterintuitive, but it’s a critical deliverability safeguard.
- The Rule: If a subscriber wants to leave, make it easy. If they can’t find the unsubscribe link, they will simply click the “Mark as Spam” button, which damages your reputation far more than an unsubscribe does. Your link must be clear and functional.
3. Maintain Consistent Volume
Spam filters look for sudden, unnatural changes in your sending behavior.
- The Rule: If you typically send 1,000 emails per week, suddenly sending 10,000 in one day will trigger a filter. If you have a brand-new sending domain, you must warm it up by starting with a small volume (50 per day) and gradually increasing the volume over 2-4 weeks.
⚡ Quick-Answer Summary: Deliverability
Question: What is the most critical factor for my Sender Reputation?
Answer: Engagement. Gmail and Outlook prioritize emails based on positive user actions: opens, clicks, and replies. The most effective way to improve your deliverability is to send personalized, relevant content to highly segmented groups (as discussed in our guide on Segmentation).
Part 4: Monitoring and Next Steps
Deliverability is an ongoing process. You must monitor your results actively.
Key Metrics to Track (in your ESP’s Analytics)
| Metric | Goal | What It Tells You |
| Hard Bounce Rate | < 0.5% | If this is high, stop sending immediately and clean your list. |
| Spam Complaint Rate | < 0.1% | If this is exceeded, your emails are guaranteed to land in spam. |
| Unsubscribe Rate | < 1.0% | If high, your content/frequency is irrelevant. |
| Click-Through Rate (CTR) | > 2% | A strong signal of positive engagement and reputation. |
Helpful External Resources for Email Deliverability
❓ Part 4: Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is the most critical factor for my Sender Reputation?
A: Engagement. Mailbox providers like Gmail and Outlook heavily prioritize emails based on positive user actions (opens, clicks, and replies). The most effective way to improve your deliverability is to send personalized, relevant content to highly segmented groups.
Q: What is a Hard Bounce?
A: A Hard Bounce means the email address is permanently invalid, non-existent, or fake. It must be immediately removed from your list, as too many hard bounces will severely damage your sender’s reputation and lead to blocking.
Q: What is SPF and DKIM?
A: SPF (Sender Policy Framework) and DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) are authentication records you publish in your domain’s DNS. They prove your identity as a legitimate sender. SPF verifies which servers are allowed to send your mail, and DKIM verifies that the email content hasn’t been tampered with.
Conclusion
Email Deliverability is the non-negotiable cost of doing business in the modern inbox. By focusing on Technical Authentication (SPF/DKIM), maintaining pristine List Hygiene (removing inactive users), and prioritizing Engagement over volume, you ensure that every part of your email marketing strategy has the chance to succeed.
Next Steps: Protect Your Inbox Placement, Calmly
You don’t need to become a technical expert to keep your emails out of spam. Start with the basics in this email deliverability guide: authenticate your domain, clean your list regularly, and send helpful messages at a steady pace.
If you’d like to connect solid deliverability with a simple, beginner-friendly online income plan, you can download my free Affiliate Marketing Starter Kit for Beginners . It’s written especially for retirees and “ageless” beginners and shows how email, content, and affiliate marketing work together.
For step-by-step training, website tools, and a friendly community, you can also learn inside Wealthy Affiliate . Many members use these same deliverability principles as they grow their lists and websites at their own pace.
This week, pick one small improvement—setting up SPF/DKIM, cleaning old inactive contacts, or sending one highly relevant email to a small segment. Small, consistent actions are what keep your emails landing in the inbox over the long term.
